What is the glycocalyx? It took until 50 years ago for the Endothelial Glycocalyx (eGC), a fragile organ that disintegrates at death, to be completely comprehended. In internal physiology, it is essential. The Microvascular Health Score can take hours to recover when there is high blood sugar or nicotine levels, among other things (MVHS). The eGC, despite being the largest organ in the body and having a surface area of a tennis court in an adult, plays a critical role in the exchange of nutrients, hormones, oxygen, and other chemicals between blood and the body’s 30 trillion cells. Adults have 60,000 miles of microcapillary length, and the eGC’s volume can be up to double that of the blood it regulates. The important point is that an unhealthy or damaged eGC can be restored, as described below.
Red Blood Cells Do Not Touch Vessel Wall
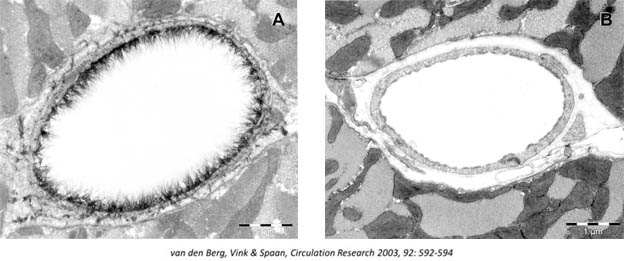
In healthy “exchange” capillaries, red blood cells (RBCs) flow in the center of the capillary while white blood cells (WBCs) compress the endothelial glycocalyx (eGC) close to the endothelial membrane without adhering or causing damage. The eGC, which has embedded antioxidant functions like superoxidase dismutase (SOD), manages inflammation unless there is an injury from trauma or infection. A thick and healthy eGC and receptors control clotting function. According to the Mystic trial, the eGC can protect the ACE II receptor on the endothelial membrane from Covid-19 invasion and mitigate pulmonary microvasculitis. More studies are ongoing. The thickness of the eGC can vary, with a range of 1-2 microns in capillaries to 4.5 microns in the carotid artery.
The major components of the eGC polysaccharide “Matrix” are:
- – Glycoproteins: selectins, integrins.
- – Glycosaminoglycans: heparin sulfate, chondroitin sulfate, hyaluronic acid
- – Proteoglycans: syndecans, glypicans.
– Endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus organelles within the endothelial cell synthesize them.
The Glycocalyx is the Teflon-lining of Blood Vessels

It took three years to learn how to preserve the polysaccharide “matrix” of the endothelial glycocalyx (eGC) before dehydrating it for electron microscopy. The eGC plays a vital role in maintaining plasma and vessel wall hemostasis in the vasculature by regulating leukocyte and thrombocyte adherence. Its composition includes plasma proteins, enzymes, enzyme inhibitors, growth factors, cytokines, amino acids, cations and water, with the latter being the largest component.
When healthy and thick, the eGC functions as a non-stick coating, preventing the adhesion of red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and lipids, mediating nitric oxide synthesis to open reserve capillaries and lower blood pressure at a systemic level. It also mitigates shear forces, especially at bifurcations and blocks microorganisms, malignant cells and albumin from entering the bloodstream.
It also contains antioxidants and mitigates inflammation and plays role in selective permeability with other biomolecules, allowing LDL in but blocks other molecules. Increased capacitance from improved eGC thickness dilutes glucose, LDL, and other lipids resulting in lower blood levels.
It has many components including Extracellular superoxide dismutase (SOD3), Angiotensin-converting enzyme, Antithrombin III, Lipoprotein Lipase, Apolipoproteins, growth factors, and Chemokines. The potential to lower HgBA1C still need to be studied.
Glycocaylx Function
A: Healthy Glycocalyx modulates Adhesion of particles of the vascular wall
- Exchange of O2/CO2, nutrients, hormones and waste
- Oxidative stress, inflammation and coagulation
- Vasodilation
- Prevents Leakage of proties and fluet into the adjacent tissues
B: Compromised Glycocalyx:
- Infiltration of flued, protiens and other blood componets into the sub endothelial space
- Reduction of capillary diameter
- Reduction in quantity of functional capilaries
- Reduced microcirculationReduction in exchange of O2/CO2, nutrients, hormones and waste
Healthy vs Damaged Glycocalyx
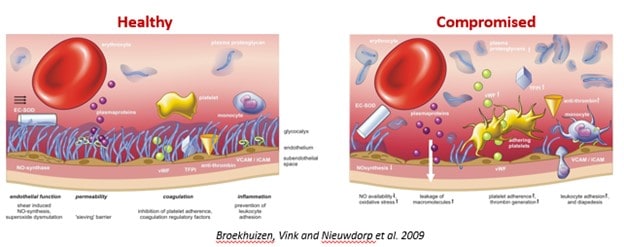
A damaged glycocalyx (eGC) can result in increased vulnerability in the vascular system. This can manifest in a number of ways, such as decreased availability of nitric oxide, increased oxidative stress, leakage of macromolecules like albumin and LDL into subendothelial spaces, increased platelet adherence and thrombin generation, and increased leukocyte adhesion, leading to inflammation and thrombotic events. In contrast, when the glycocalyx is healthy, blood flow can increase as needed, for example during physical activity or mental exertion.
Damage to the endothelial glycocalyx (eGC) can lead to a decrease in capillary beds. However, this can be improved by using the solution at the end of this article.
When the eGC is damaged, it can cause a decrease in blood flow and a descending cycle of tissue and organ dysfunction. This can result in residual capillaries with severely damaged eGC becoming sticky, resulting in little or no blood flow.
The following can damage the eGC:
- Lack of proper micronutrition, specifically glycomimetic compounds found in essential Mediterranean and Pan Asian plant-based diets
- Hyperglycemia
- Nicotine
- Epigenetics
- Aging (but it can be reversed)
- Obesity (in obese trial, high-risk patients without symptoms were already missing 45% of the exchange capillaries)
- Stress hormones (cortisol, norepinephrine, epinephrine, and pharmaceutical equivalents)
- Medications that increase insulin resistance
- Sepsis with toxins and covid microvasculitis can also shred the eGC leading to loss of “exchange” capillaries, perivascular edema, thrombosis, low pressure pulmonary edema, and organ ischemia. (in the ICU- “sick” covid patients have loss 95% of the “exchange” capillaries)
- Other disease states.
Signs of decreasing organ blood flow — early warning signs
More than 85 clinical research studies by researchers and hospitals around the world confirm that a single hidden problem—a weakened glycocalyx and microvascular system—begins with early warning signs:
- Type 2 Diabetes
- High Blood Pressure
- Erectile Dysfunction
- Severe PMS
- Cold Hands and Feet
- Leg Cramps
- Skin Problems
- Hair Thinning
- Fatigue
- Neuropathy
- Lack of Focus
- Memory Loss
- Certain Eye Problems
- Hearing Loss
- Slow Wound Healing
And now researchers know that a weakened glycocalyx—revealed by those early warning signs—begins a spiral of organ starvation, and is linked to several diseases and conditions:
- Hypertension
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Heart Disease
- Kidney Disease
- Stroke
- Dementia
- Septic Shock
- Inflammatory Disorders
- Cancer Metastasis
- Long Haul COVID-19
- Complications
But the eGC and blood flow can be restored with Endocalyx Pro!
Endocalyx Pro™ for Healthier Glycocalyx
Endocalyx Pro is a supplement made with Laminaria Japonica, a brown seaweed extract that is certified to have a minimum extract rate of 85% of the compound fucoidan sulfate. Fucoidan sulfate is a hybrid of heparan sulfate and chondroitin sulfate, and has a high binding affinity for heparanase. It repairs the glycocalyx and prevents breakdown by inhibiting heparanase activity. In addition to the fucoidan sulfate, Endocalyx Pro also contains high molecular weight hyaluronan which is essential for providing the glycocalyx with its structural stability and dimension.
The supplement also contains glucosamine sulfate, a high dose of 1,500 mg (vegetarian) which provides the building blocks for glycocalyx synthesis. Research has confirmed that glucosamine at this concentration boosts endothelial cell glycocalyx production.
Endocalyx Pro also contains a next-generation proprietary blend of polyphenol and flavonoids consisting of the most efficacious fruits and vegetables clinically shown to produce antioxidant activity. These ingredients include Olive (fruit) extract, artichoke (leaf) extract, red and white grapes (fruit) extract, superoxide dismutase (from bitter melon concentrate), and catalase (also from bitter melon concentrate). These ingredients are clinically effective in protecting the glycocalyx.
To restore the eGC and previously collapsed capillary beds, Whole Medicine Approaches in addition to Endocalyx Pro is recommended. This includes:
- Lifestyle factors such as healthy BMI and food choices (low CHO especially simple sugars, moderate fat and protein; portion size, lowering insulin stimulation (insulin resistance), lowered Set Point in the hypothalamus)
- Fitness, aerobic and resistance
- Behaviors such as smoking cessation, sleep hygiene, CPAP if necessary: therapists using Cognitive Behavioral Strategies with practitioners trained in Motivational Interviewing
- Modulating stress (hormones) with healthy emotional and relationship health using advanced Cognitive Behavioral Strategies with practitioners trained in Motivational Interviewing, Mindfulness training and Meditation
- Medications such as newer diabetic medications can improve the eGC: e.g., glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RA), sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT-2i)
- Spiritual connectedness (ie medicine)
One example of the effectiveness of Endocalyx Pro is a woman with a leg pre-amputation ischemic ulcer that was getting worse until she started taking Endocalyx Pro. She experienced quick development of healthy granulation tissue (recovery of collapsed capillary beds and blood flow) and improved blood pressure (increase in blood capacity) within 2 weeks.
Learn more about Endocalyx Pro here.
(Editor’s Note: This article is based on original authorship of Dr. Don McGee.)